- view的测量流程
- view的布局流程
- view的绘制流程
- 自定义view
ViewRoot和DecorView
我的理解:ViewRoot是View的管理者,DecorView是顶级的View,它包括了title view和content view两部分 Android ViewRootImpl 解析_Lerendan的博客-CSDN博客_android viewrootimplAndroid 知识体系学习目录_Lerendan的博客-CSDN博客
确定View的尺寸规格
系统内部通过Measure来进行View的测量。 对于顶级View:MeasureSpec由窗口的尺寸和其自身的LayoutParams来共同确定 对于普通View:MeasureSpec由父容器的MeasureSpec和其自身的LayoutParams来共同确定
直接继承View自定义控件-wrap_content
需要从写onMeasure方法并设置wrap_content时的自身大小。
//解决继承View实现控件wrap_content失效通法
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//MeasureSpec测量规格
//getMode 测量模式
//getSize 规格大小
int widthSpecMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if(widthSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST&&heightSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(200,200);
}else if(widthSpecMode== MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(200,heightSpecSize);
}else if(heightSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize,200);
}
}


如何获取View的宽高
在onCreate、onStart、onResume中均不能获取到某个View的宽高信息。View的measure过程和Activity的生命周期不同步。
1.View#onWindowFocusChanged
View已经初始化完成。当Activity的窗口得到和失去焦点时均会被调用此方法。 
2.view.post
通过post将一个runnable投递到消息队列的尾部。 
3.ViewTreeObserver

Layout过程
- Layout过程的作用:View Group用来确定子元素的位置
- ViewGroup在onLayout中遍历所有的子元素并调用其layout方法
- layout方法确定View本身的位置;onLayout方法确定所有子元素的位置
view#layout
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT) != 0) {
onMeasure(mOldWidthMeasureSpec, mOldHeightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
int oldL = mLeft;
int oldT = mTop;
int oldB = mBottom;
int oldR = mRight;
//setFrame方法设定view的四个顶点位置,此后View在父容器的位置就确定了
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
//调用onLayout方法是父容器用来确定子元素的位置
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
if (shouldDrawRoundScrollbar()) {
if(mRoundScrollbarRenderer == null) {
mRoundScrollbarRenderer = new RoundScrollbarRenderer(this);
}
} else {
mRoundScrollbarRenderer = null;
}
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners != null) {
ArrayList<OnLayoutChangeListener> listenersCopy =
(ArrayList<OnLayoutChangeListener>)li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners.clone();
int numListeners = listenersCopy.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) {
listenersCopy.get(i).onLayoutChange(this, l, t, r, b, oldL, oldT, oldR, oldB);
}
}
}
final boolean wasLayoutValid = isLayoutValid();
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_IS_LAID_OUT;
if (!wasLayoutValid && isFocused()) {
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_WANTS_FOCUS;
if (canTakeFocus()) {
// We have a robust focus, so parents should no longer be wanting focus.
clearParentsWantFocus();
} else if (getViewRootImpl() == null || !getViewRootImpl().isInLayout()) {
// This is a weird case. Most-likely the user, rather than ViewRootImpl, called
// layout. In this case, there's no guarantee that parent layouts will be evaluated
// and thus the safest action is to clear focus here.
clearFocusInternal(null, /* propagate */ true, /* refocus */ false);
clearParentsWantFocus();
} else if (!hasParentWantsFocus()) {
// original requestFocus was likely on this view directly, so just clear focus
clearFocusInternal(null, /* propagate */ true, /* refocus */ false);
}
// otherwise, we let parents handle re-assigning focus during their layout passes.
} else if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_WANTS_FOCUS) != 0) {
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_WANTS_FOCUS;
View focused = findFocus();
if (focused != null) {
// Try to restore focus as close as possible to our starting focus.
if (!restoreDefaultFocus() && !hasParentWantsFocus()) {
// Give up and clear focus once we've reached the top-most parent which wants
// focus.
focused.clearFocusInternal(null, /* propagate */ true, /* refocus */ false);
}
}
}
if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_NOTIFY_AUTOFILL_ENTER_ON_LAYOUT) != 0) {
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_NOTIFY_AUTOFILL_ENTER_ON_LAYOUT;
notifyEnterOrExitForAutoFillIfNeeded(true);
}
notifyAppearedOrDisappearedForContentCaptureIfNeeded(true);
}view#onLayout
onLayout方法是一个空方法。因为具体的布局的onLayout实现会不同(View和ViewGroup均没有实现)
/**
* Called from layout when this view should
* assign a size and position to each of its children.
*
* Derived classes with children should override
* this method and call layout on each of
* their children.
* @param changed This is a new size or position for this view
* @param left Left position, relative to parent
* @param top Top position, relative to parent
* @param right Right position, relative to parent
* @param bottom Bottom position, relative to parent
*/
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
}LinearLayout#onLayout
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
layoutVertical(l, t, r, b);
} else {
layoutHorizontal(l, t, r, b);
}
}void layoutVertical(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
final int paddingLeft = mPaddingLeft;
int childTop;
int childLeft;
// Where right end of child should go
final int width = right - left;
int childRight = width - mPaddingRight;
// Space available for child
int childSpace = width - paddingLeft - mPaddingRight;
final int count = getVirtualChildCount();
final int majorGravity = mGravity & Gravity.VERTICAL_GRAVITY_MASK;
final int minorGravity = mGravity & Gravity.RELATIVE_HORIZONTAL_GRAVITY_MASK;
switch (majorGravity) {
case Gravity.BOTTOM:
// mTotalLength contains the padding already
childTop = mPaddingTop + bottom - top - mTotalLength;
break;
// mTotalLength contains the padding already
case Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL:
childTop = mPaddingTop + (bottom - top - mTotalLength) / 2;
break;
case Gravity.TOP:
default:
childTop = mPaddingTop;
break;
}
//遍历所有子元素
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child == null) {
childTop += measureNullChild(i);
} else if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
final int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
final LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp =
(LinearLayout.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int gravity = lp.gravity;
if (gravity < 0) {
gravity = minorGravity;
}
final int layoutDirection = getLayoutDirection();
final int absoluteGravity = Gravity.getAbsoluteGravity(gravity, layoutDirection);
switch (absoluteGravity & Gravity.HORIZONTAL_GRAVITY_MASK) {
case Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL:
childLeft = paddingLeft + ((childSpace - childWidth) / 2)
+ lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin;
break;
case Gravity.RIGHT:
childLeft = childRight - childWidth - lp.rightMargin;
break;
case Gravity.LEFT:
default:
childLeft = paddingLeft + lp.leftMargin;
break;
}
if (hasDividerBeforeChildAt(i)) {
childTop += mDividerHeight;
}
childTop += lp.topMargin;
setChildFrame(child, childLeft, childTop + getLocationOffset(child),
childWidth, childHeight);
childTop += childHeight + lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child);
i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);
}
}
}ConstrainLayout#onLayout
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
if (DEBUG) {
System.out.println(mLayoutWidget.getDebugName() + " onLayout changed: " + changed + " left: " + left + " top: " + top
+ " right: " + right + " bottom: " + bottom + " (" + (right - left) + " x " + (bottom - top) + ")");
}
final int widgetsCount = getChildCount();
final boolean isInEditMode = isInEditMode();
for (int i = 0; i < widgetsCount; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
LayoutParams params = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
ConstraintWidget widget = params.widget;
if (child.getVisibility() == GONE && !params.isGuideline && !params.isHelper && !params.isVirtualGroup && !isInEditMode) {
// If we are in edit mode, let's layout the widget so that they are at "the right place"
// visually in the editor (as we get our positions from layoutlib)
continue;
}
if (params.isInPlaceholder) {
continue;
}
int l = widget.getX();
int t = widget.getY();
int r = l + widget.getWidth();
int b = t + widget.getHeight();
if (DEBUG) {
if (child.getVisibility() != View.GONE
&& (child.getMeasuredWidth() != widget.getWidth()
|| child.getMeasuredHeight() != widget.getHeight())) {
int deltaX = Math.abs(child.getMeasuredWidth() - widget.getWidth());
int deltaY = Math.abs(child.getMeasuredHeight() - widget.getHeight());
if (deltaX > 1 || deltaY > 1) {
System.out.println("child " + child + " measuredWidth " + child.getMeasuredWidth()
+ " vs " + widget.getWidth() + " x measureHeight " + child.getMeasuredHeight()
+ " vs " + widget.getHeight());
}
}
}
child.layout(l, t, r, b);
if (child instanceof Placeholder) {
Placeholder holder = (Placeholder) child;
View content = holder.getContent();
if (content != null) {
content.setVisibility(VISIBLE);
content.layout(l, t, r, b);
}
}
}
final int helperCount = mConstraintHelpers.size();
if (helperCount > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < helperCount; i++) {
ConstraintHelper helper = mConstraintHelpers.get(i);
helper.updatePostLayout(this);
}
}
}getMeasureWidth 与 getWidth 的本质区别
关于View的getWidth()和getMeasuredWidth()的知识总结 - 掘金getMeasuredWidth() 与getWidth()分别对应于视图绘制 的 measure 与 layout 阶段。 getWidth()返回的是右边坐标减去左边坐标,这要在布局之后才能确定它们的坐标,也就是说在布局后onLayout()方法里面才能调用getWidth()来获取。 getMeasuredWidth()返回的是此视图的原始测量宽度。所以说getMeasuredWidth()是对View上的内容进行测量后得到的View内容占据的宽度。 一般情况下,getMeasuredWidth()和getWidth()获得的结果是一样的,但是如果在父布局的onLayout()方法或者此View的onDraw()方法里调用measure(0,0);(measure中的参数的值你自己可以定义)的话,两者的结果可能会不同。
为什么onMeasure和onLayout过程要分开
[Android 自定义 View] —— 深入总结 onMeasure、 onLayout
onDraw过程
view#draw
@CallSuper
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
final int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags;
mPrivateFlags = (privateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) | PFLAG_DRAWN;
/*
* Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed
* in the appropriate order:
*
* 1. Draw the background
* 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
* 3. Draw view's content
* 4. Draw children
* 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
* 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
* 7. If necessary, draw the default focus highlight
*/
// Step 1, draw the background, if needed
int saveCount;
drawBackground(canvas);
// skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case)
final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;
boolean horizontalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_HORIZONTAL) != 0;
boolean verticalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_VERTICAL) != 0;
if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) {
// Step 3, draw the content
onDraw(canvas);
// Step 4, draw the children
// 递归调用子元素的draw
dispatchDraw(canvas);
drawAutofilledHighlight(canvas);
// Overlay is part of the content and draws beneath Foreground
if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas);
}
// Step 6, draw decorations (foreground, scrollbars)
onDrawForeground(canvas);
// Step 7, draw the default focus highlight
drawDefaultFocusHighlight(canvas);
if (isShowingLayoutBounds()) {
debugDrawFocus(canvas);
}
// we're done...
return;
}ViewGroup#dispatchDraw
/**
* dispatchDraw()的作用是绘制父视图中包含的子视图,该函数的本质作用是给不同的子视图分配合
* 适 的 画 布 (Canvas),至于子视图如何绘制,则又递归到View类 的 draw()函数中。应用程序一般不需要
* 重 载 dispatchDrawO函数,而只需要在onLayout()中为子视图分配合适的大小, dispatchDraw()将根据前
* 面分配的大小调整Canvas的内部剪切区,并作为绘制子视图的画布。所有的ViewGroup实例的内部绘
* 制基本上都是如此,这就是为什么具体的ViewGroup实例不需要重载dispatchDraw()的原因。
* 特例constrainLayout重写了dispatchDraw()
*/
@Override
protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) {
final int count = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
int flags = mGroupFlags;
/**
* 判 断 mGroupFlags中是否设置FLAG—RUN—ANIMATION标识,该标识并不是该ViewGroup的
* “动画标识”,而是 该ViewGroup “布局动画标识”。动画标识指的是一个View自身的动画,而布局动
* 画只存在于ViewGroup对象中,指的是该ViewGroup在显示内部的子视图时,为内部子视图整体设置
* 的 动 画 。 典 型 的 例 子 就 是 , 应 用 程 序 可 以 在 X M L 文 件 中 的 LinearLayout标 签 中 设 置
* android:layoutAnimation属性,从而使 该LinearLayout的子视图在显示时出现逐行显示、随机显示、落
* 下等不同的动画效果,而这些效果正是在本步骤实现的。关于动画的详细过程见后面小节,本节只分析
* 没有动画的情况。
*/
if ((flags & FLAG_RUN_ANIMATION) != 0 && canAnimate()) {
final boolean cache = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_ANIMATION_CACHE) == FLAG_ANIMATION_CACHE;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE) {
final LayoutParams params = child.getLayoutParams();
attachLayoutAnimationParameters(child, params, i, count);
bindLayoutAnimation(child);
if (cache) {
child.setDrawingCacheEnabled(true);
child.buildDrawingCache(true);
}
}
}
final LayoutAnimationController controller = mLayoutAnimationController;
if (controller.willOverlap()) {
mGroupFlags |= FLAG_OPTIMIZE_INVALIDATE;
}
controller.start();
mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_RUN_ANIMATION;
mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_ANIMATION_DONE;
if (cache) {
mGroupFlags |= FLAG_CHILDREN_DRAWN_WITH_CACHE;
}
if (mAnimationListener != null) {
mAnimationListener.onAnimationStart(controller.getAnimation());
}
}
/**
* 处理padding属性。该属性是ViewGroup特有的,程序员只能给一个ViewGroup设 置padding,
* 而不能给一个View设 置padding。如 果ViewGroup包 含padding值 ,则 CLIP_PADDINT—MASK标识将
* 存在。对 于 View系统而言,当绘制到某个View时, View系统并不区分该View是一个具体的Veiw还
* 是一个ViewGroup实例,都会在View.draw()函数中调用dispatchDraw(canvas),参 数 Canvas的绘制区原
* 点坐标是该View内部区域的左上角, Canvas的剪切区仅仅是根据scrool值进行了剪切。由于padding
* 是 ViewGroup所特有的属性,因此ViewGroup的 dispatchDraw()需要对该属性进行自身的处理。
* 源码中首先调用canvas.save()保 存 当 前Canvas内部状态,然 后 调 用canvas.clipRect()进行剪切。在
* 执 行 dispatchDraw()函数前, Canvas的剪切区已经根据scroll值进行了剪切,剪切坐标的原点是View自
* 身的左上角,所以此处仅仅需要从左边加paddingLeft,从上边加paddingTop,从右边减paddingRight,
* 从下边减paddingBottom。
* 执行后,就会根据padding的值缩小剪切区。这里需要注意,缩小的仅仅是剪切区,也就是用户在
* 屏幕上看到的区域,而 ViewGmup本身的大小没有变化。
*/
int saveCount = 0;
final boolean clipToPadding = (flags & CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK) == CLIP_TO_PADDING_MASK;
if (clipToPadding) {
saveCount = canvas.save();
canvas.clipRect(mScrollX + mPaddingLeft, mScrollY + mPaddingTop,
mScrollX + mRight - mLeft - mPaddingRight,
mScrollY + mBottom - mTop - mPaddingBottom);
}
/**
* 清 除 mPrivateFlags的 DRAW_ANIMATION标 识 ,因为接下来就会绘制视图了;同时清除
* mGroupFlags的 FLAG—INVALIDATED_REQUJRIED标 识 , 因 为 接 来 绘 制 后 就 意 味 着 已 经 满 足
* "RECURIED” 这个需求了。
*/
// We will draw our child's animation, let's reset the flag
mPrivateFlags &= ~DRAW_ANIMATION;
mGroupFlags &= ~FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED;
boolean more = false;
final long drawingTime = getDrawingTime();
/**
* 使 用 for()循环,针 对 该ViewGroup的子视图逐个调用drawChild()函数。在一般情况下,绘制
* 子 视 图 的 顺 序 是 按 照 子 视 图 被 添 加 的 顺 序 逐 个 绘 制 , 但 应 用 程 序 可 以 重 载 ViewGmup的
* getChildDrawingOrder()函数,提供不同的顺序。关 于 drawChild()的内部过程见后面小节
*/
if ((flags & FLAG_USE_CHILD_DRAWING_ORDER) == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null) {
more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime);
}
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = children[getChildDrawingOrder(count, i)];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null) {
more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime);
}
}
}
// Draw any disappearing views that have animations
/**
* 绘 制 mDisappearingChildren列表中的子视图。这个变量需要着重解释一下,当 从 ViewGroup
* 中 removeView()时,指 定 的View对象会从mChildren变量中移除,因此,当进行消息派发时,被删除
* 的 View就绝不会获得用户消息。当被删除的View对象包含一个移除动画时,则 该 View会被添加到
* mDisappearingChildren列表中,从而使得在进行dispatchDraw()时,该 View依然会被绘制到屏幕上,直
* 到动画结束,在动画期间,用户虽然能够看到该视图,但却无法点击该视图,因为它已经从mChildren
* 列表中被删除,消息处理时会认为没有该View的存在。
*/
if (mDisappearingChildren != null) {
final ArrayList<View> disappearingChildren = mDisappearingChildren;
final int disappearingCount = disappearingChildren.size() - 1;
// Go backwards -- we may delete as animations finish
for (int i = disappearingCount; i >= 0; i--) {
final View child = disappearingChildren.get(i);
more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime);
}
}
if (clipToPadding) {
canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount);
}
// mGroupFlags might have been updated by drawChild()
flags = mGroupFlags;
/**
* 6、 重新检查 mGroupFlags 中是否包含 FLAG_INVALIDATED_REQURIED 标识,因为 drawChild()
* 调用后,可能需要重绘该ViewGroup,如果需要,贝U调 用 invalidate()发起一个重绘请求。
*/
if ((flags & FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED) == FLAG_INVALIDATE_REQUIRED) {
invalidate();
}
/**
* 7 、本步骤与第Q 步是对称的,第+ 步中会先处理“布局动画”,而本步骤则处理布局动画是否完
* 成,如果完成,发 送 一 个 Handler消息。该 消 息 是 一 个Runnable对象,其 作 用 是 回 调ViewGroup中
* AnimationListener接 口 的onAnimationEnd()函数,通知应用程序布局动画完成了。
*/
if ((flags & FLAG_ANIMATION_DONE) == 0 && (flags & FLAG_NOTIFY_ANIMATION_LISTENER) == 0 &&
mLayoutAnimationController.isDone() && !more) {
// We want to erase the drawing cache and notify the listener after the
// next frame is drawn because one extra invalidate() is caused by
// drawChild() after the animation is over
mGroupFlags |= FLAG_NOTIFY_ANIMATION_LISTENER;
final Runnable end = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
notifyAnimationListener();
}
};
post(end);
}
}自定义View
自定义View是一个综合技术体系,涉及
- View的层次结构
- 事件分发机制
- View的工作原理
自定义View的分类
继承View
继承特定的View,TextView扩展功能
自定义ViewGroup
继承特定的ViewGroup LinearLayout
继承View重写onDraw
继承ViewGroup派生特殊的Layout
继承特定的View
继承特定的ViewGroup
自定义View注意事项
- 直接继承View和ViewGroup,需要考虑wrap_content和padding
- 不要在View中使用handler,view内部有post方法
- View中有线程或动画,需要及时停止,防止内存泄漏。
View#onDetachedFromWindow包含此View的Activity退出或者当前View被remove时,此方法会被调用。 View#onAttachedToWindow包含此View的Activity启动此方法会被调用。
- View带有嵌套滑动,要解决滑动冲突。
一、继承View重写onDraw方法
实现不规则的效果,最为灵活。
- 实现构造方法
- 重写onDraw
- 处理wrap_content失效
- 处理padding失效
- 自定义属性
绘制流程 View的体系结构 View和ViewGroup
1.实现构造方法
2.重写onDraw
package com.hnucm.chapter4_1.ui;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
/**
* 第一种:继承View重写onDraw方法
* 1.实现构造方法
* 2.重写onDraw
* 3.处理wrap_content失效
* 4.处理padding失效
* 5.自定义属性
*
*/
public class CircleView extends View {
private int mColor= Color.BLUE;
private Paint mPaint= new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
public CircleView(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public CircleView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public CircleView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
public CircleView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
init();
}
private void init(){
mPaint.setColor(mColor);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
int width=getWidth();
int height=getHeight();
int radius=Math.min(width,height)/2;
canvas.drawCircle(width/2,height/2,radius,mPaint);
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<com.hnucm.chapter4_1.ui.CircleView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="@color/teal_200"/>
</LinearLayout> margin生效,margin属性由父容器控制
margin生效,margin属性由父容器控制 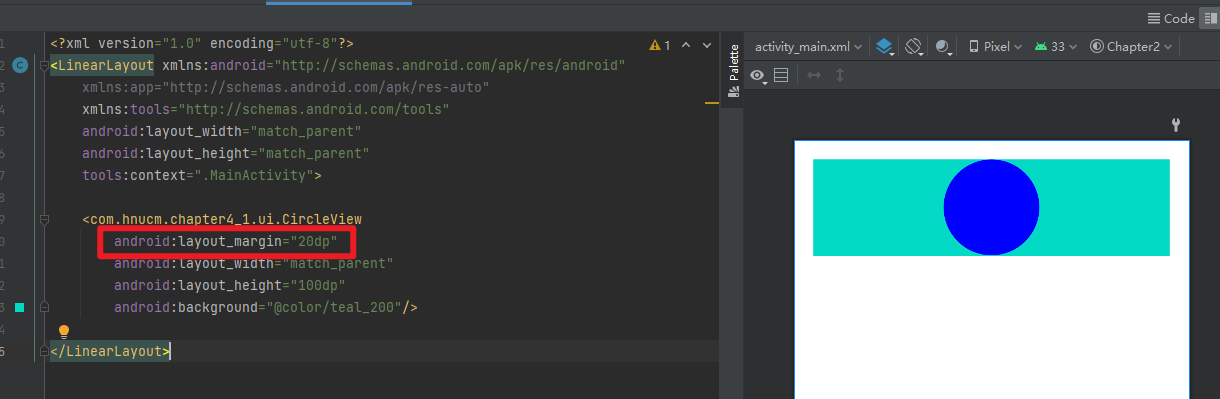 padding无效
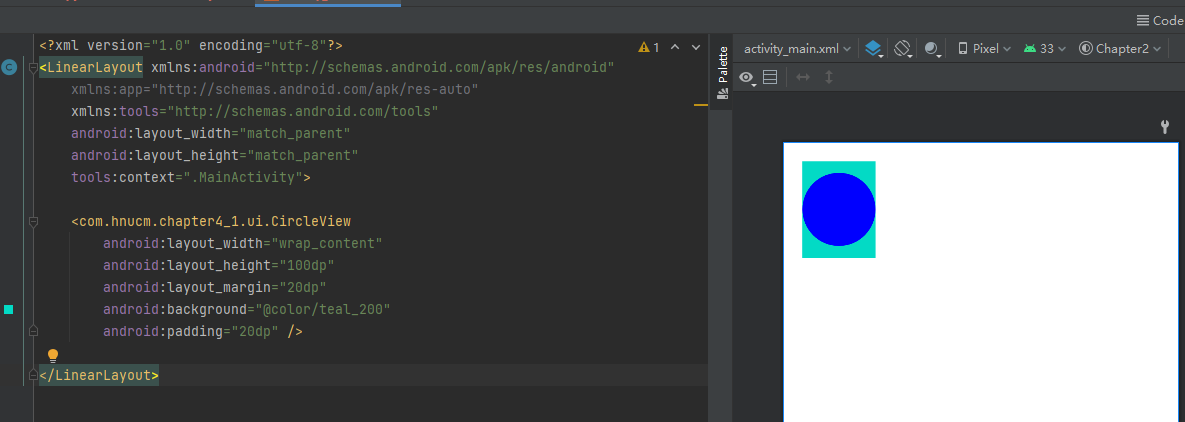
padding无效 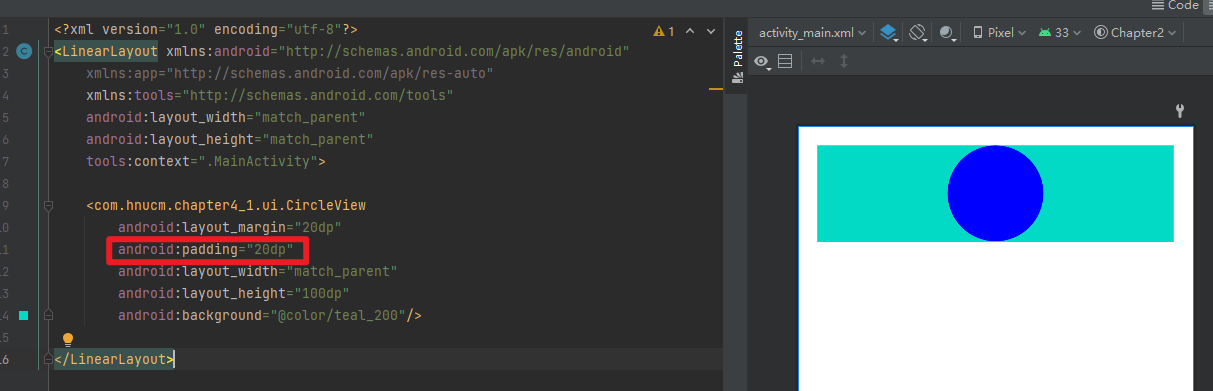 wrap_content无效
wrap_content无效 
3.处理wrap_content失效
//解决继承View实现控件wrap_content失效通法
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//MeasureSpec测量规格
//getMode 测量模式
//getSize 规格大小
int widthSpecMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if(widthSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST&&heightSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(200,200);
}else if(widthSpecMode== MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(200,heightSpecSize);
}else if(heightSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize,200);
}
}
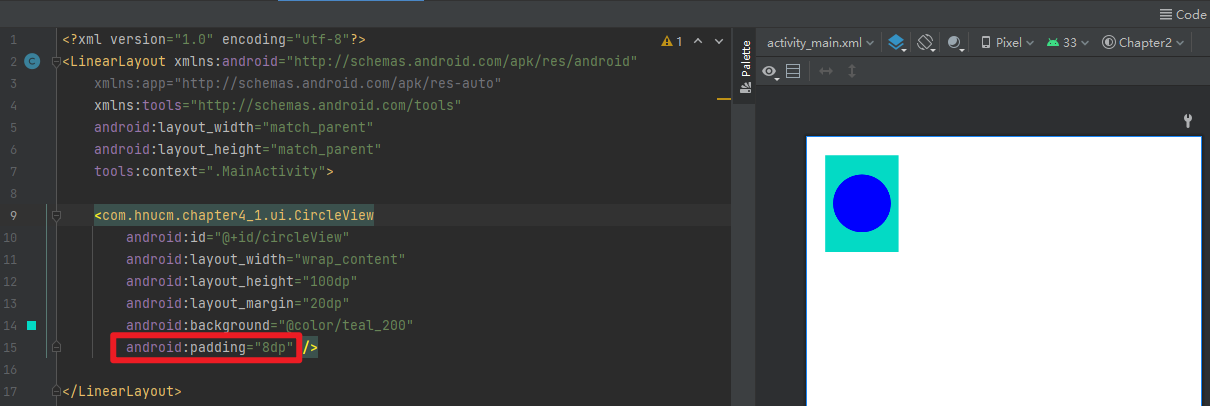
4.处理padding失效
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
final int paddingLeft=getPaddingLeft();
final int paddingRight=getPaddingRight();
final int paddingTop=getPaddingTop();
final int paddingBottom=getPaddingBottom();
int width=getWidth()-paddingLeft-paddingRight;
int height=getHeight()-paddingTop-paddingBottom;
int radius=Math.min(width,height)/2;
canvas.drawCircle(paddingLeft+width/2,paddingTop+height/2,radius,mPaint);
}
5.自定义属性
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="CircleView">
<attr name="circle_color" format="color"/>
</declare-styleable>
</resources>

6.CircleView
package com.hnucm.chapter4_1.ui;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.WindowId;
import androidx.annotation.AnyThread;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
import com.hnucm.chapter4_1.R;
/**
* 第一种:继承View重写onDraw方法
* 1.实现构造方法
* 2.重写onDraw
* 3.处理wrap_content失效
* 4.处理padding失效
* 5.自定义属性
*
*/
public class CircleView extends View {
private final static String TAG="MainActivity";
private int mColor= Color.BLUE;
private Paint mPaint= new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
public CircleView(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public CircleView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context,attrs,0);
}
public CircleView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
TypedArray a=context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CircleView);//加载属性集合
mColor=a.getColor(R.styleable.CircleView_circle_color,Color.BLUE);//解析颜色属性
a.recycle();//释放资源
init();
}
public CircleView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
init();
}
private void init(){
mPaint.setColor(mColor);
}
//解决继承View实现控件wrap_content失效通法
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//MeasureSpec测量规格
//getMode 测量模式
//getSize 规格大小
int widthSpecMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if(widthSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST&&heightSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(200,200);
}else if(widthSpecMode== MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
Log.e(TAG, "heightSpecSize: "+heightSpecSize );
setMeasuredDimension(200,heightSpecSize);
}else if(heightSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
Log.e(TAG, "widthSpecSize: "+widthSpecSize );
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize,200);
}
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
final int paddingLeft=getPaddingLeft();
final int paddingRight=getPaddingRight();
final int paddingTop=getPaddingTop();
final int paddingBottom=getPaddingBottom();
int width=getWidth()-paddingLeft-paddingRight;
int height=getHeight()-paddingTop-paddingBottom;
int radius=Math.min(width,height)/2;
canvas.drawCircle(paddingLeft+width/2,paddingTop+height/2,radius,mPaint);
}
}二、继承ViewGroup派生特殊的Layout
实现自定义布局,较为复杂,需要处理ViewGroup的测量和布局两个过程,并同时处理子元素的测量和布局过程。 实现类似ViewPager的效果,更规范的实现参考源码ViewPager的onMeasure和onLayout方法
package com.hnucm.chapter3_3.ui;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.VelocityTracker;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.Scroller;
public class HorizontalScrollViewEx extends ViewGroup {
private static final String TAG = "HorizontalScrollViewEx";
private int mChildrenSize;
private int mChildWidth;
private int mChildIndex;
// 分别记录上次滑动的坐标
private int mLastX = 0;
private int mLastY = 0;
// 分别记录上次滑动的坐标(onInterceptTouchEvent)
private int mLastXIntercept = 0;
private int mLastYIntercept = 0;
private Scroller mScroller;
private VelocityTracker mVelocityTracker;
public HorizontalScrollViewEx(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public HorizontalScrollViewEx(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public HorizontalScrollViewEx(Context context, AttributeSet attrs,
int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
init();
}
private void init() {
mScroller = new Scroller(getContext());
mVelocityTracker = VelocityTracker.obtain();
}
//外部拦截法
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
boolean intercepted = false;
int x = (int) event.getX();
int y = (int) event.getY();
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: {
intercepted = false;
if (!mScroller.isFinished()) {
mScroller.abortAnimation();
intercepted = true;
}
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: {
int deltaX = x - mLastXIntercept;
int deltaY = y - mLastYIntercept;
if (Math.abs(deltaX) > Math.abs(deltaY)) {
intercepted = true;
} else {
intercepted = false;
}
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: {
intercepted = false;
break;
}
default:
break;
}
Log.d(TAG, "intercepted=" + intercepted);
mLastX = x;
mLastY = y;
mLastXIntercept = x;
mLastYIntercept = y;
return intercepted;
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(event);
int x = (int) event.getX();
int y = (int) event.getY();
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: {
if (!mScroller.isFinished()) {
mScroller.abortAnimation();
}
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: {
int deltaX = x - mLastX;
int deltaY = y - mLastY;
//处理滑动事件,水平滑动
scrollBy(-deltaX, 0);
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: {
int scrollX = getScrollX();
int scrollToChildIndex = scrollX / mChildWidth;
mVelocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000);
float xVelocity = mVelocityTracker.getXVelocity();
if (Math.abs(xVelocity) >= 50) {
mChildIndex = xVelocity > 0 ? mChildIndex - 1 : mChildIndex + 1;
} else {
mChildIndex = (scrollX + mChildWidth / 2) / mChildWidth;
}
mChildIndex = Math.max(0, Math.min(mChildIndex, mChildrenSize - 1));
int dx = mChildIndex * mChildWidth - scrollX;
smoothScrollBy(dx, 0);
mVelocityTracker.clear();
break;
}
default:
break;
}
mLastX = x;
mLastY = y;
return true;
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int measuredWidth = 0;
int measuredHeight = 0;
final int childCount = getChildCount();
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSpaceSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpaceSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
//没有子元素 宽高设为0
if (childCount == 0) {
setMeasuredDimension(0, 0);
// 高度设为wrap_content 高度即为第一个子元素的高度
} else if (heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
final View childView = getChildAt(0);
measuredHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpaceSize, childView.getMeasuredHeight());
// 宽度设置为wrap_content 宽度即为所有子元素的宽度之和
} else if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
final View childView = getChildAt(0);
measuredWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth() * childCount;
setMeasuredDimension(measuredWidth, heightSpaceSize);
} else {
// 如果都为wrap_content 高度即为第一个子元素的高度、宽度即为所有子元素的宽度之和
final View childView = getChildAt(0);
measuredWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth() * childCount;
measuredHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
setMeasuredDimension(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childLeft = 0;
final int childCount = getChildCount();
mChildrenSize = childCount;
// 遍历子元素
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
final View childView = getChildAt(i);
if (childView.getVisibility() != View.GONE) {
final int childWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
mChildWidth = childWidth;
// 确定子元素的位置
// 未考虑margin和padding
childView.layout(childLeft, 0, childLeft + childWidth,
childView.getMeasuredHeight());
childLeft += childWidth;
}
}
}
private void smoothScrollBy(int dx, int dy) {
mScroller.startScroll(getScrollX(), 0, dx, 0, 500);
invalidate();
}
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
if (mScroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
scrollTo(mScroller.getCurrX(), mScroller.getCurrY());
postInvalidate();
}
}
@Override
protected void onDetachedFromWindow() {
mVelocityTracker.recycle();
super.onDetachedFromWindow();
}
}